How can I activate DMARC with STRATO?
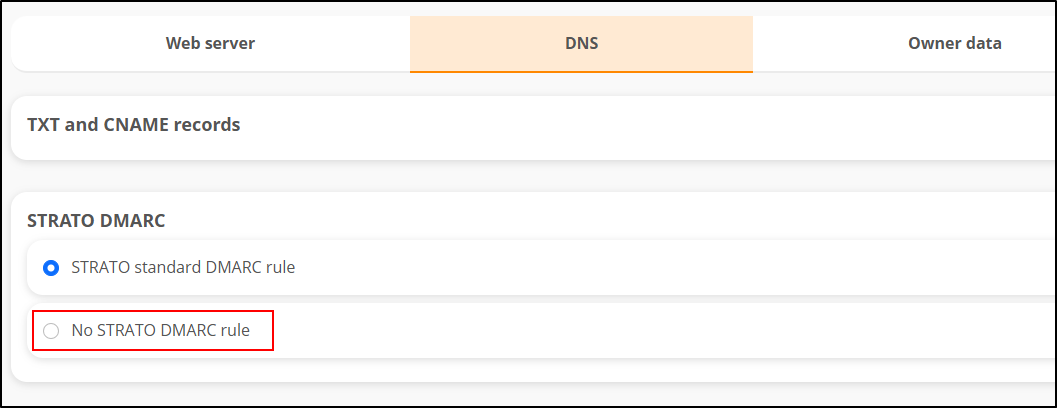
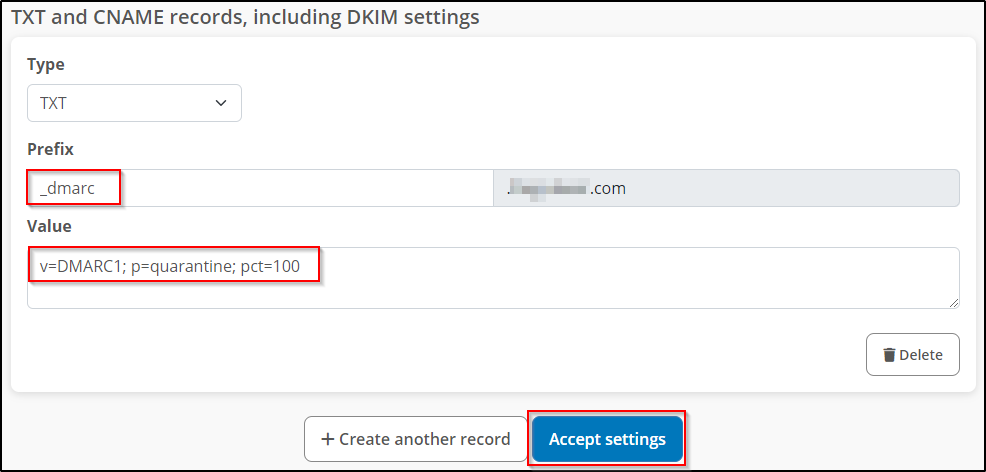
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) is a mechanism designed to reduce the misuse of e-mails, as occurs in the context of phishing. With the correct DMARC and SPF settings, you can prevent someone from receiving an email that was supposedly sent in your name but did not actually come from you. The respective settings and the DKIM signatures are intended as information for the receiving mail server. The receiving mail server is therefore able to recognise whether an email is fake or not. If it is a fake email, the mail server can react accordingly using the DMARC policy you have specified. When you send an email, the recipient's mail server analyses this information. The receiving mail server uses the DKIM signature and the SPF information to recognise whether the email really comes from you. If this is not the case, but unknown third parties are using your sender address for criminal purposes, the email is handled according to the policy stored with DMARC. More and more cyber criminals are trying to lull their targets into a false sense of security and deceive them. They write emails in the name of other people and organisations (e.g. also in the name of STRATO GmbH). DMARC offers a mechanism that provides an email recipient (more precisely, the receiving mail server) with a procedure for handling emails depending on the result of the DKIM and SPF check. Therefore, there must be at least one DNS entry for DKIM or SPF for the sender domain (i.e. for "MyDomain.com" in the case of the sender myAddress@MyDomain.com). DNS is the Domain Name Service, the "Internet telephone book", in which IP addresses are also assigned to domain names, among other things). 1. DKIM is already activated at STRATO, all messages that you send via STRATO are already provided with a DKIM signature. You don't need to do anything else. The only requirement is that you send the message with your own sender address. (It becomes more difficult when third-party providers send e-mails in your name. Then this provider must also sign the messages in your name). 2.SPF rule: In most cases, it is sufficient to set the setting to “No STRATO SPF rule” or leave it as it is. However, if you require a special SPF rule, for example when using an external email provider, please configure the setting manually as described in this article. 3. DMARC is already activated at STRATO. If you want to deactivate this, then select the option "No STRATO DMARC rule". If you want to setup DMARC manually, you can use the following settings: Type: TXT Prefix: _dmarc Click on Accept settings. 4. Repeat this process for each domain whose emails are to be handled by DMARC.What is DMARC?
What do I need to know about DMARC?
Phishing messages are often sent with so-called Header-From from known domains (own, PayPal, Ebay, STRATO etc.), so we strongly recommend that you make the appropriate settings.
DMARC cannot prevent someone from sending e-mails in your name. But you can use your DMARC record to prevent someone from receiving these forgeries and believing them to be genuine.
By the way: In the special case that someone allegedly sends you messages from your own domain, you yourself are the recipient and therefore even benefit from your own DMARC settings.
Not all mail servers respond to your DMARC entry. But more are responding every day.
If you forward received emails, e.g. to report them to STRATO, you must observe the following:
Use a filter rule with the action "Forward mail to" in your STRATO e-mail inbox for forwarding. This ensures that the forwarded mail is forwarded in such a way that the DKIM and SPF checks on the receiving mail server do not fail.
If you forward an email via your email programme in the name of the original sender, it may be sent as a new email via your email inbox. As a result, this email may be recognised as a forgery by the receiving mail server (making it subject to the DMARC policy of the original sender). More and more email service providers are checking DMARC strictly and rejecting messages that do not pass the check.Why should I use DMARC?
DMARC checks the structure and information of these e-mails. If an e-mail does not meet the requirements, it can be directly marked as suspicious or even rejected. We recommend that you set the spam protection setting to "Place spam in spam folder", as a rejected e-mail cannot be retrieved in the mailbox at a later date - it simply does not arrive there in the first place.What can DMARC do?
Like DKIM and SPF, the DMARC rules (policy) are stored publicly in the DNS. There is a TXT record with the prefix _dmarc, which must be filled with certain values. DMARC offers you three different procedures if the SPF _and_ DKIM check both return a negative result:
1. Policy “none”: The e-mail is delivered unchanged. However, there may be a report for the error (if the mail server supports this).
2. Policy “quarantine”: The e-mail is treated as spam. As the recipient, you determine what this means. With STRATO, you can choose between four treatments for received emails:
Never reject spam (= delivery to the inbox like a normal message)
Mark the subject of spam mails in the inbox
Place spam in the spam folder
Always reject spam: The message is rejected, the sender receives a corresponding message
3. “reject”: Messages are rejected, the sender receives a corresponding message
Other important settings for DMARC:What do I have to do to activate DMARC at STRATO?
Value: v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; pct=100
(Instead of "quarantine", write "none" or "reject" depending on the selected policy. See “What can DMARC do?”) Was this article helpful?